The Special Legislative Procedures: Consent
Aside from the ordinary legislative procedure, there are a number of special legislative procedures that are used less often. The two most common are the Consent Procedure and Consultation.
The Consent Procedure (formally known as the assent procedure)
Under the consent procedure, the Commission makes a proposal which must be either rejected or accepted by the European Parliament by absolute majority. Importantly, the Parliament cannot make any amendments, it must reject or accept the proposal as it is. However, rejection of a proposal constitutes a veto for the Parliament, as the Council cannot take any decisions without the Parliament’s ‘consent’.
While it may seem that Parliament has a straightforward accept or decline role, in reality it is slightly more nuanced, as in stating what it will reject, Parliament can often imply what it would accept. The Parliament can offer an interim report during the process to highlight what it would agree to.
Some of the key policy areas covered by the consent procedure are –
- Membership of the Union
- Arrangements for withdrawal from the Union
- Association agreements
- Agreements establishing a specific institutional framework
- Agreements with important budgetary implications
The consent procedure in diagrammatic form…
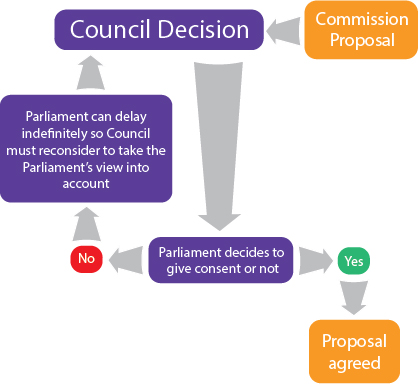
Consent key facts:-
- Commission makes a proposal, Parliament must accept or reject
- Use reserved for important decisions such as EU membership agreements
Consent key features:-
- Parliament has a veto
- Parliament cannot make amendments, but in saying ‘no’ it can offer information on what it would say yes to
- Power rests with both Council and Parliament, so this procedure can be seen to be broadly supranational
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |
Leave a Reply